
Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal Birth Control:
Your Complete Guide to Options and Answers
Hormonal birth control utilizes hormones naturally present in a woman’s body such as estrogen and progesterone. They block the release of eggs from the ovaries, thin the lining of the uterus, and thicken the mucus in the cervix to prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
6 Kinds of Hormonal Birth Control
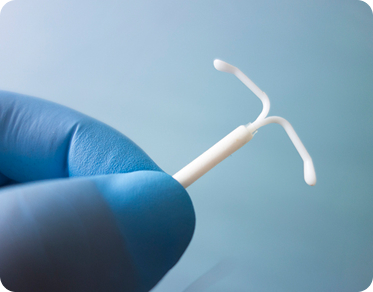
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
Intrauterine devices are long-acting reversible contraceptives that can prevent pregnancy by releasing progestin into the uterus to prevent sperm from fertilizing the egg. They are inserted into the uterus or as implants placed just under the skin. The failure rate is less than one in one hundred. IUDs can stay inserted and be effective for up to eight years. After removing an IUD, for most people, the menstrual cycle returns to normal within a month. Research suggests for those trying to conceive, that many women typically become pregnant between three months to one year after getting the IUD taken out. This can be influenced by a number of factors, such as health and age.
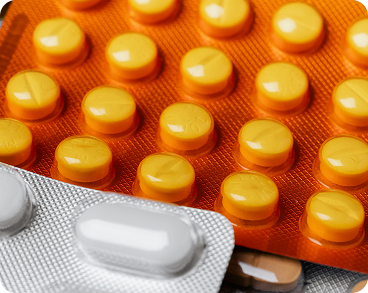
Birth Control Pills
Birth control pills, also simply known as “the pill,” are a short-acting option taken orally, that can also prevent pregnancy. They have a success rate of 99% when taken correctly. These pills are only prescribed by a medical professional, with several brands offered in pharmacies. These must be taken orally daily around the same time each day. Once prescribed, you take the pill on the first day of your period. Consistently take it for one month while using another form of birth control, such as condoms, to prevent pregnancy. After one month, your body will have adjusted, and the pill will be effective on its own at this point.
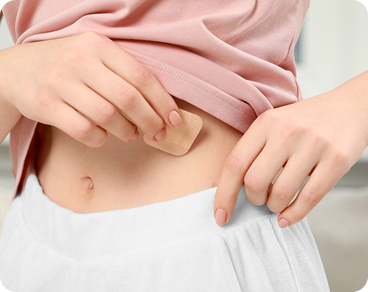
Stick On Patches
Stick-on patches are an adhesive patch typically put on less exposed areas of skin, for example, your lower abdomen or back. The patch is applied on the first day of your period and is changed every seven days. You skip the patch on the fourth week to allow for your menstruation. It has similar side effects to the pill and is guaranteed effectiveness with correct use. You can increase your risk of pregnancy should the patch be removed or unchanged. Check the patch regularly and use backup contraception, like barrier methods, if it is no longer sticking and needs to be replaced.

Vaginal Rings
A vaginal ring is a small, flexible ring that is inserted into the vagina and stays in place. You can insert the ring manually but will need to get a prescription to purchase this kind of birth control. As a hormonal contraception, the ring lines the vagina with estrogen and progestin to prevent ovulation and to thicken the cervical mucus so sperm cannot reach the egg. Like the stick-on patch, it is inserted for 21 days (about 3 weeks) and removed for one week to allow menstruation. You then insert a new vaginal ring.
There are also reusable vaginal rings which can be removed and washed then reinserted and last for a year. Insertion is like inserting a tampon, sticking the ring in as far as you can, and leaving it there. It may dislodge if straining during a bowel movement or sexual intercourse. The ring does not cause discomfort, though, and has fewer side effects than other hormonal contraception.
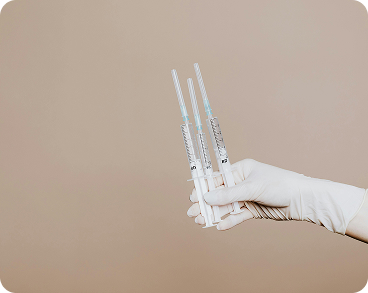
Birth Control Injections
Known by its brand name, Depo-Provera, this is a contraceptive injection that works like the previous birth control options, suppressing ovulation, thinning the uterine lining, and thickening the cervical mucus. A healthcare provider must administer the shot, which you will need to get every three months. The main risk associated with the birth control shot is a delay in your return to fertility. It can take up to ten months for ovulation to start again.
Birth Control Implants
An implant (also known by its brand name Nexplanon) is a small rod that is inserted under the skin in the upper inner arm by your healthcare provider. Implants contain the hormone progestin, and are effective for at least 3 years, but can be removed earlier if needed. The implant is one of the most effective forms of birth control- if implanted correctly, the implant is 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
What Are the Side Effects of Hormonal Birth Control?
Hormonal birth control side effects vary for each user. You should call your doctor immediately or seek urgent treatment if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Note that due to the hormonal changes in your body caused by these types of birth control, namely the increase in estrogen and progestin hormones, you may experience the following:
Disclaimer:
This is for informational purposes only. For medical advice or diagnosis, consult a professional.
When exploring birth control methods, it’s essential to research various options and consult a healthcare professional to make an informed decision that aligns with your unique needs and lifestyle. Each individual’s body and circumstances are different, so it’s important to choose a method that feels right for you—free from external pressures or influences. Remember, this is a personal choice that directly impacts your health and well-being. Prioritizing your comfort and understanding will empower you to make the best decision for your reproductive health.
Birth Control Resources
View moreFEMM Health
FEMM Health- Telemed
FEMM Health
Have Questions About Hormonal Birth Control?
Ask Our Confidential Chatbot!

